|
ELECTROMAGNETIC
SPECTRUM
k
= kilo = 10 3
M = mega = 10 6
G = giga = 10 9
T =
tera = 10 12
P = peta = 10 15
E = exa = 10 18
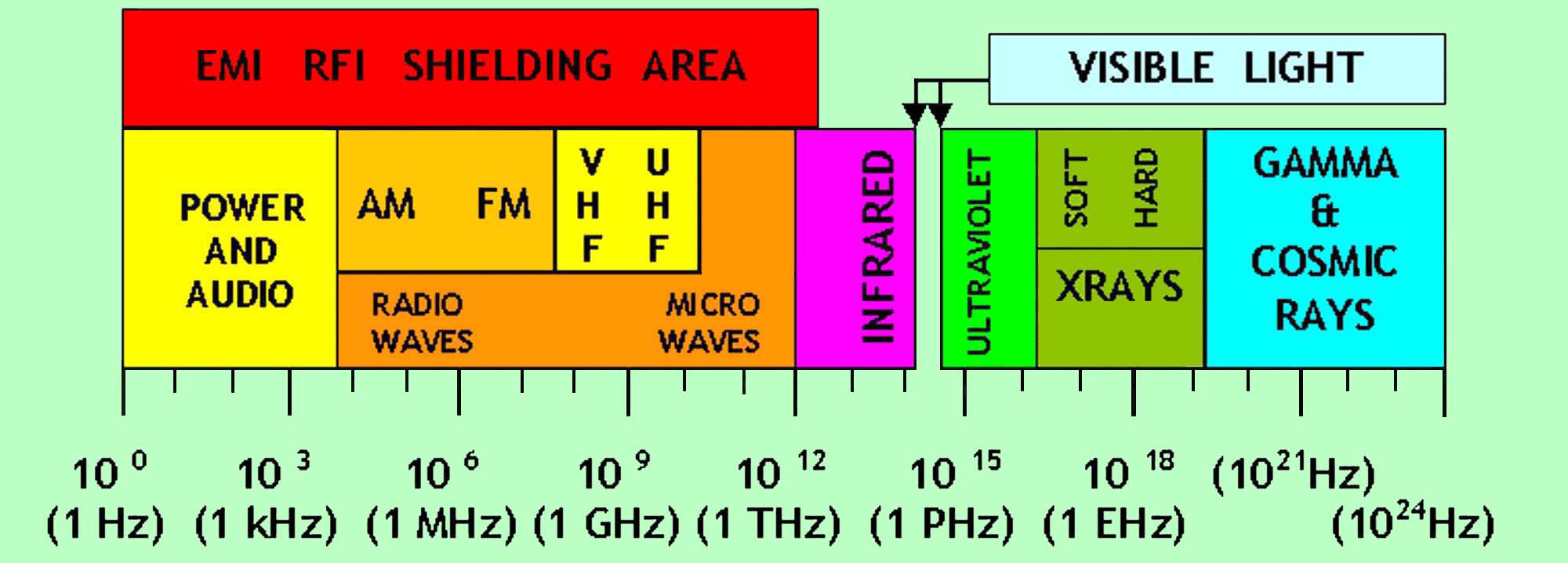
RADIO WAVES
BAND
NAME
FREQUENCY
LENGHT
4
VLF
3 kHz a 30
kHz
100 km a 10 km
5
LF
30 kHz a 300
kHz
10 km a
1 km
6
MF
300 kHz a
3
MHz
1 km a 100 m
7
HF
3 MHz a 30
MHz
100 m a 10
m
8
VHF
30 MHz a 300
MHz
10 m
a 1 m
9
UHF
300 MHz a 3
GHz
1 m a
10 cm
10
SHF
3 GHz a 30
GHz
10 cm a
1 cm
11
EHF
30 GHz a 300
GHz
1 cm a
1 mm
12
-
300 GHz a 3000
GHz 1
mm a 0,1 mm
RADIO WAVES PROPAGATION
THE SKY WAVE
At frequencies below 30 MHz is carried on by means of the sky
wave. This is a wave that, on leaving the transmitting antenna, would travel on
out into empty space if it were not for the fact that under certain conditions
it can be sufficiently reflected or refracted, high up in the earth's atmosphere,
to reach the earth again at distances varying from zero to about 4000 km from
the transmitter. By successive reflections at the earth's surface and in the
upper atmosphere, communication can be established over the maximum possible
terrestrial distances.
THE IONOSPHERE
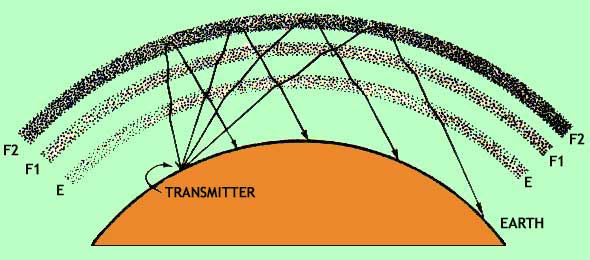
The region in which the waves are bent back to earth is
called the ionosphere. This is a section of the upper atmosphere in which the
air pressure is so low that "free" electrons and ions can move for a
long time without getting close enough to each other to be attracted together
and thus recombine into a neutral atom. A wave entering a region in which there
are many free electrons will be affected in much the same way as one entering a
region of differing dielectric constant; that is, its direction of travel will
be shifted.
IONIZATION REGION
An elevated
number of sunspots
increases the ionization of the high region and create favorable
conditions for the propagation of the electromagnetic waves with a
better reflection.
D
region-located between 50
km and 90 km - maximum ionization
at midday disappear in the sunshine.
E
region-located between 100
km and 150 km - maximum ionization
at midday minimum at midnight, increasing at dawn.
Sporadic
E-ocated between 100
km and 120 km .
F1
region - located between 150
km and 250 km - in the night
existing an only F
that divides in F1
- F2 during the day.
F2
region - located between 250
km and 500 km - maximum ionization
at midday decreasing slowly until the dawn. Could reach the maximum of 350 km in
winter and 500 km in summer. |